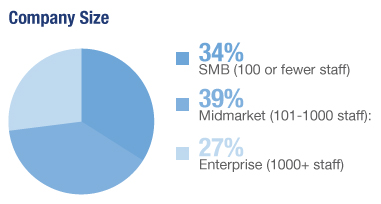
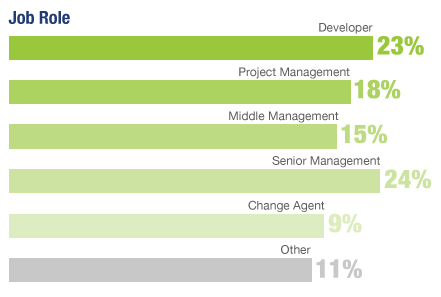
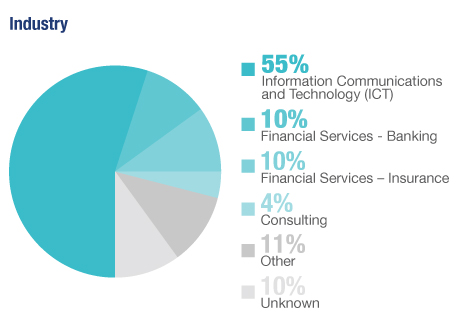
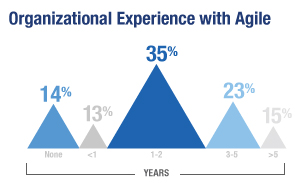
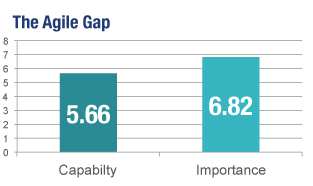
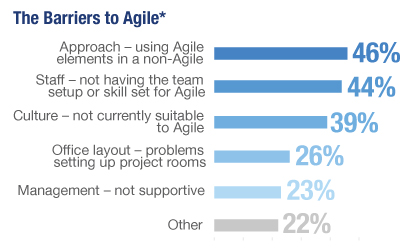
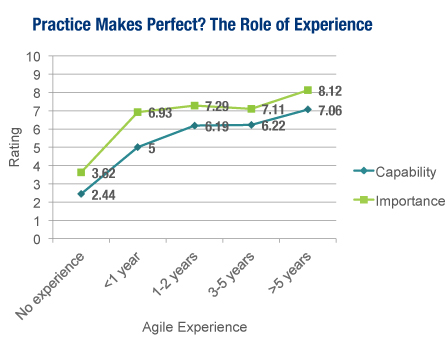
| Benefits by Correlation |
Correlation |
| Fit to product needs & the ability to adapt |
0.320 |
| Fit to product needs & time to market |
0.311 |
| Reduced risk & ability to adapt |
0.279 |
| Lower costs & time to market |
0.268 |
| Reduced risk & greater collaboration |
0.259 |
| Reduced risk & fit to product needs |
0.245 |
|
Figure 2: Benefits with at least a moderate level of correlation, i.e. > 0.2. Note that correlation ranges from +1 between (perfect correlation) to –1 (perfect negative correlation). 0 indicates no relationship.
|
Understanding the relationship between two benefits of Agile is helpful to get a sense of which benefits go well with one another. But alone, they leave an unclear picture of how these various benefits of Agile relate to broader business benefits. Consequently, we grouped these benefits together to create related “factors”, or broader categories of benefits. Using factor analysis, we found that the benefits listed in our survey could be loosely grouped into the following three factors:
- Software quality
- Speed and agility
- Resources: saving time and money
“Software quality” includes four variables (or benefits): better fit of features of product needs, reduced risk, greater collaboration, and ability to adapt to changing priorities. “Speed and agility” includes time to market and ability to adapt. “Resources” include lower costs and faster time to market, which could be interpreted as saving staff time as well as satisfying the market with releasing products faster. These three factors show the true breadth of Agile benefits: effectiveness (software quality), efficiency (speed and agility) and money (resources).*** “Greater Collaboration” has a 0.30 correlation and 0.001 significance with Agile importance and has a 0.35 correlation and 0.000 significance with Agile capability. The “ability to adapt to changing priorities” has a 0.35 correlation and 0.000 significance with Agile importance and has a 0.31 correlation and 0.001 significance with Agile capability.
**Statistically significant at the 0.05 level, i.e. p<.05.
***To see the factor scores, see the Appendix.